Steel Plant Lubrication

Lubrication in an integrated steel plant is a major challenge with numerous types of lubricants and various types of equipment. The steel plant equipment work under various operating parameters; like from extreme heavy load to very high speed, low temperatures to high temperatures, dusty polluted environment to humid acid environment. Therefore proper selection of lubricant is much essential for smooth operation in steel plants and reliability of equipment.
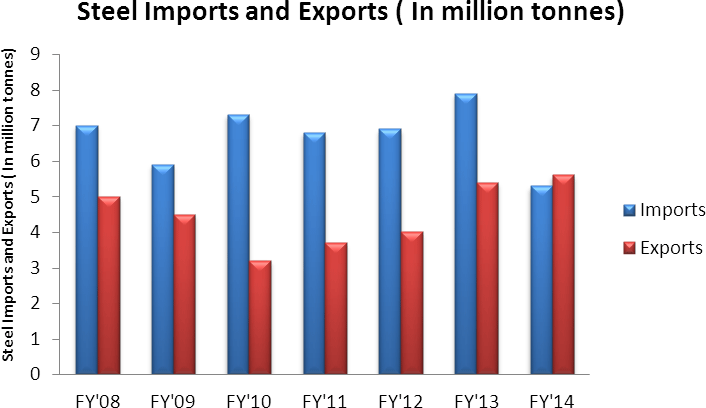 India at present with 77 MMT is the 4th largest steel producer globally. In 2012, India became a net importer of steel, mainly special grades. By 2016, India is expected to become world’s 2nd largest crude steel producer. Fast urbanization will be the driving force for India’s steel industry growth. Total crude steel production rose at a CAGR of 7.9 percent over the last five years to reach 81.54 MT in FY14 where as finished steel production increased 4.1 percent to 85.0 MT in FY14. By 2020, Indian steel sector will witness emergence of 5-6 players controlling 65
India at present with 77 MMT is the 4th largest steel producer globally. In 2012, India became a net importer of steel, mainly special grades. By 2016, India is expected to become world’s 2nd largest crude steel producer. Fast urbanization will be the driving force for India’s steel industry growth. Total crude steel production rose at a CAGR of 7.9 percent over the last five years to reach 81.54 MT in FY14 where as finished steel production increased 4.1 percent to 85.0 MT in FY14. By 2020, Indian steel sector will witness emergence of 5-6 players controlling 65
70% of total production and will emerge as one of the leading exporter of steel globally along with China. Over the last few years, import dependency has decreased due to growth in domestic production. However the per capita consumption of steel in India remains low which suggests that there is still a high potential for growth. Over FY08–FY14, consumption has of steel has expanded at a CAGR of 6 percent. Steel consumption is expected to grow at an average rate of 6.8 per cent, reaching 113.3 MTPA by FY17. Infrastructure is India’s largest steel consumer, accounting for 63 percent of total consumption in FY12. Engineering and fabrication is the next largest consumer, with 22 percent of total consumption.
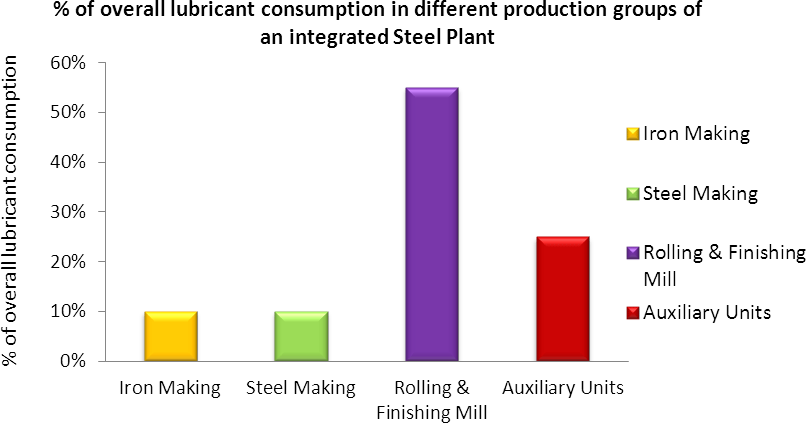
 An integrated steel plant comprises of four major groups such as Iron Making, Steel Making, Rolling and Finishing and Auxiliary Units. The equipment and the working environment in each of these groups differ significantly and hence the requirements of the lubricants used are also different. The Iron making group includes plants like raw material blending & blending yard, beneficial plant, sinter plant, coke ovens and blast furnaces etc. The equipment in general are required to work under high temperature dusty (abrasive) and corrosive environment. The equipment used for crushing and screening application are subjected to high impact as well. The speeds are lower. The steel making group includes plant like LD Furnaces, continuous casters as well as lime plant etc. The equipment are subjected to very high temperature, dusty (abrasive) and corrosive environment. The other working conditions in this group are similar to those in the iron making group. The rolling and finishing group includes Hot Strip Mill, Cold Rolling Mill, Primary Boom Bar Mill, Bar and Wire Rod Mill and Merchant Mill. The equipment in rolling and finishing group are subjected to high impact loads , water and scale ingress, high temperature near reheating furnaces and higher speed and unit loads.
An integrated steel plant comprises of four major groups such as Iron Making, Steel Making, Rolling and Finishing and Auxiliary Units. The equipment and the working environment in each of these groups differ significantly and hence the requirements of the lubricants used are also different. The Iron making group includes plants like raw material blending & blending yard, beneficial plant, sinter plant, coke ovens and blast furnaces etc. The equipment in general are required to work under high temperature dusty (abrasive) and corrosive environment. The equipment used for crushing and screening application are subjected to high impact as well. The speeds are lower. The steel making group includes plant like LD Furnaces, continuous casters as well as lime plant etc. The equipment are subjected to very high temperature, dusty (abrasive) and corrosive environment. The other working conditions in this group are similar to those in the iron making group. The rolling and finishing group includes Hot Strip Mill, Cold Rolling Mill, Primary Boom Bar Mill, Bar and Wire Rod Mill and Merchant Mill. The equipment in rolling and finishing group are subjected to high impact loads , water and scale ingress, high temperature near reheating furnaces and higher speed and unit loads.
 In Steel plants equipment reliability & better maintenance practices are very important which directly affects the productivity & equipment Health. Specific Maintenance cost is to the tune of roughly around Rs 1500 per tonnes of crude steel. This is about 10-15 % of the total production cost. Proper lubrication can obviate various maintenance problems leading to smooth operation of steel plants. Cost of Lubricants is only a tiny fraction of maintenance cost. But improper lubrication can cause more than 30% of the breakdowns. Procuring superior quality of lubricant may slightly increase the spare cost however this will be rewarding in terms of trouble free working, reduced spares and optimum cost of maintenance.
In Steel plants equipment reliability & better maintenance practices are very important which directly affects the productivity & equipment Health. Specific Maintenance cost is to the tune of roughly around Rs 1500 per tonnes of crude steel. This is about 10-15 % of the total production cost. Proper lubrication can obviate various maintenance problems leading to smooth operation of steel plants. Cost of Lubricants is only a tiny fraction of maintenance cost. But improper lubrication can cause more than 30% of the breakdowns. Procuring superior quality of lubricant may slightly increase the spare cost however this will be rewarding in terms of trouble free working, reduced spares and optimum cost of maintenance.
While selecting lubricant for steel plants equipment these factors must be taken into consideration. Generally OEMs recommend the type and grade of the lubricant based on the design, speed and load parameters of the equipment. However in the absence of OEM recommendation or in case the recommended grade is not performing, a set of codes are to be made as guidelines by considering the afore-mentioned operational factors and select the lubricants accordingly. While selecting lubricant for an application, two very important aspects are to be looked at, namely, the factors concerning engineering requirements and the factors concerning requirements pertaining to the service condition. The majority of engineering requirements are met by selecting proper viscosity of the oil (called lubricant grade) while the service condition requirements are met by selecting proper additive package for the lubricant ( called lubricant type).
| Process Group | % of Total Maintenance Cost in the Process Plant | % of Total Lubricant Consumed in the Plant |
|---|---|---|
| Iron Making | 11% | 10% |
| Steel Making | 15% | 10% |
| Rolling Mills | 52% | 55% |
| Auxillary Units | 22% | 25% |
The factors concerning engineering requirement includes load, speed, surface finish of the interacting surfaces and rise in temperature etc. The problems posed by the service condition of the application are addressed by selecting a suitable additive system and appropriate base oil for the lubricant. Different additive combinations are used for providing protection against rusting, oxidation, scuffing, corrosion and foaming etc. Various categories of base oils available are mentioned as below:
 The base oil trend in steel plants is currently shifting from Group I to II due to the higher oxidation stability, thermal stability and high Viscosity Index and lower sulphur content of Group II base oil compared to Group I. Further Group II formulated oils have excellent demulsibility properties which is an essential parameter for steel mill bearing oils. Most of the lubricants such as hydraulic oil, gear oil, circulating oil and turbine oil used in a steel plant are now being formulated with Group II base oil. The use of synthetic oil in steel plants is limited to certain compressor oil and few gear oils (critical gear box with severe shock load and high temperature).
The base oil trend in steel plants is currently shifting from Group I to II due to the higher oxidation stability, thermal stability and high Viscosity Index and lower sulphur content of Group II base oil compared to Group I. Further Group II formulated oils have excellent demulsibility properties which is an essential parameter for steel mill bearing oils. Most of the lubricants such as hydraulic oil, gear oil, circulating oil and turbine oil used in a steel plant are now being formulated with Group II base oil. The use of synthetic oil in steel plants is limited to certain compressor oil and few gear oils (critical gear box with severe shock load and high temperature).
Some of the major suppliers of lubricants in Indian steel plants are IOCL, HPCL, BPCL, Shell, Mobil and Quaker Chemicals. Various types of lubricant grades are used in a steel plant. Those grades are hydraulic oil, industrial gear oils, compressor oils, film bearing oils, compounded oils, high demulsibility circulating oils(With and without EP), turbine oils, metal working fluids (mineral based, semi-synthetic and synthetics- heat type & emulsion type), wire rope and open gear compounds , automotive crankcase oils, process oils like cold and hot rolling oils, rust preventive oils, mill greases ,high temperature greases, multipurpose greases and speciality lubricants doped with MoS2 or graphite.
| Base Oil Category | Sulfur (%) | Saturates (%) | 2007 Global Basestock Distribution | Viscosity Index (VI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group I (solvent refined) | >0.03 | and/or | <90 | 66% | 80 to 120 |
| Group II (hydrotreated) | <0.03 | and | >90 | 20% | 80 to 120 |
| Group III (hydrocracked) | <0.03 | and | >90 | 5% | >120 |
| Group IV | PAO Synthetic Lubricants | ||||
| Group V | All other base oils not included in Groups I, II, III or IV | ||||
 All these grades of lubricants used in steel plants can be categorized in to five classes such as machinery lubricants, hydraulic oils, metal working fluids, automotive lubricants and process oils. Machinery Lubricants include spindle oil, way oil, cylinder oil, straight mineral oil, turbine oil, mist oils, gear oil, mill bearing circulating oil, black oils and greases. Spindle oils are low viscosity oil for machine toll bearings working at very high speeds. Way oils are heavy duty EP oil with oiliness additive which are used in machine tool way. These oils have good stick slip property, for Cylinder oil are high viscous fluids used for application in worm gears and steam cylinders. Black oils are dark, heavy, tacky oils which are meant for open gears, skids and chains lubrication. Circulating oils are used for the lubrication of back up rolls, NTM work rolls of rolling mills. Inhibited type highly refined (Group II base) are used for the turbines and blowers of steel plants. These oils are fortified with antioxidant, antirust, antifoam additives and possess very high thermal stability with, oxidation stability etc. Industrial gear oils are highly refined mineral oils fortified with EP additive and are used for lubrication of gearboxes, mill drives and pinions. Mist oils are lubricants which possess good misting properties, low stray mist, no gumming properties, which are used in rolling element bearing and slippers of universal spindle. Greases of different base type (Ca/Li/Al/Poly Urea/Clay base) with or without additive/filler are used for the lubrication of antifriction bearings and couplings of steel plants.
All these grades of lubricants used in steel plants can be categorized in to five classes such as machinery lubricants, hydraulic oils, metal working fluids, automotive lubricants and process oils. Machinery Lubricants include spindle oil, way oil, cylinder oil, straight mineral oil, turbine oil, mist oils, gear oil, mill bearing circulating oil, black oils and greases. Spindle oils are low viscosity oil for machine toll bearings working at very high speeds. Way oils are heavy duty EP oil with oiliness additive which are used in machine tool way. These oils have good stick slip property, for Cylinder oil are high viscous fluids used for application in worm gears and steam cylinders. Black oils are dark, heavy, tacky oils which are meant for open gears, skids and chains lubrication. Circulating oils are used for the lubrication of back up rolls, NTM work rolls of rolling mills. Inhibited type highly refined (Group II base) are used for the turbines and blowers of steel plants. These oils are fortified with antioxidant, antirust, antifoam additives and possess very high thermal stability with, oxidation stability etc. Industrial gear oils are highly refined mineral oils fortified with EP additive and are used for lubrication of gearboxes, mill drives and pinions. Mist oils are lubricants which possess good misting properties, low stray mist, no gumming properties, which are used in rolling element bearing and slippers of universal spindle. Greases of different base type (Ca/Li/Al/Poly Urea/Clay base) with or without additive/filler are used for the lubrication of antifriction bearings and couplings of steel plants.
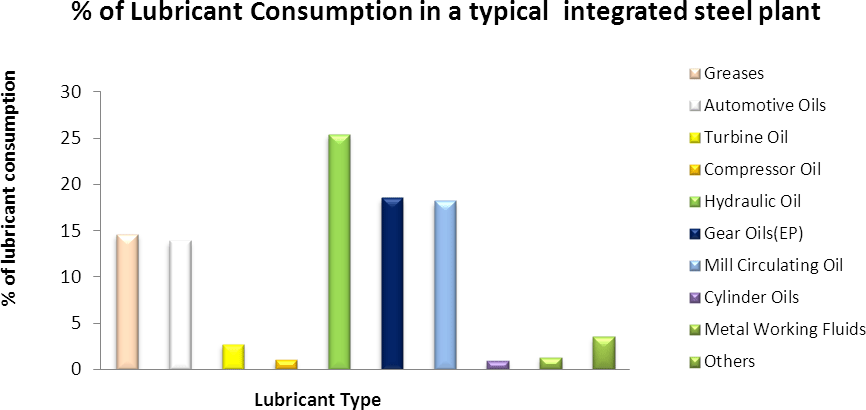 In Steel plants various types of hydraulic fluid such as antiwear hydraulic fluid, fire resistant fluids and high water based fluids are used. Antiwear hydraulic oils are low viscosity refined oil with friction modifier for the fluid power system, with antirust, antifoam, antiwear additives, etc. Fire resistant fluids are water in oil emulsions having made of water glycols, organic esters and phosphate ester for protection against fire. High water based fluids (95/5) are also used for fire resistant application.
In Steel plants various types of hydraulic fluid such as antiwear hydraulic fluid, fire resistant fluids and high water based fluids are used. Antiwear hydraulic oils are low viscosity refined oil with friction modifier for the fluid power system, with antirust, antifoam, antiwear additives, etc. Fire resistant fluids are water in oil emulsions having made of water glycols, organic esters and phosphate ester for protection against fire. High water based fluids (95/5) are also used for fire resistant application.
Process Lubricants in steel plants include slushing oil, rolling oils, pickler oils, mould oil and wire drawing compounds. Slushing oils are antirust, inhibited, light oil for sheet protection .Rolling oils are made of synthetic oil, semi-synthetic oil, fatty oil which is used for roll bite lubrication . Pickler oils are light mineral oil with rust inhibitor for sheet protection after pickling. Wire drawing compound are soaps with fillers for wire drawing application. Metal Working Fluids include soluble oils and neat cutting oils. Soluble oils are lubricating oil with emulsifiers which are used in water hydraulics and light machine tool operations. Cutting oils are chemical and petroleum base products for use in cutting, grinding and drawing, etc. Automotive grades are used in locos, mobile equipments, IC engines and HEV equipments.
Designation of service parameters:
Before selection of a lubricant for a specific application in a steel plant various process parameters like speed, load, temperature and moisture content must be designated. The load in steel plant equipment can be classified into five categories as per recommended % of c-ratings of AFMBA chart (Cn) which are as follows:
Load W: Normal (1), Medium (2), Heavy (3), Very Heavy (4), Impact (5)
- It the actual load , W is as per recommended % of c-ratings as per AFMBA chart(Cn), i.e W<=Cn
- Cn<= W<=1.2 Cn ?
- 1.2Cn <=W <= 1.3 Cn ?
- 1.3 Cn <=W <= 1.4 Cn ?
- W >= 1.4 Cn
Example:
(1): Centrifugal pump, fan and blower (2): Transfer table rolls, Vibratory screens (3): Rod Mill and Bal Mills, gearboxes (4): Mill drive gearboxes, sheet straightening machine (5): Roughing and Finishing mill work rolls, Hammer mills and crushers.
| Type of equipment | Load & Speed | Type of equipment | Load & Speed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Centrifugal pumps fans and blowers | 1,9 | Vibrator screen | 2,6 |
| Transfer table rolls | 2,8 | Gearboxes | 3,8 |
| Rod and ball mills | 3,6 | Mill drive gearboxes | 4,8 |
| Finishing mill work roll, ROT rolls | 5,8 | NTM drive system | 1,8 |
| Roughing mill work rolls | 5,7 | Mixing drum, kiln | 4,6 |
| Hammer mill and crusher | 5,9 | Hydraulic pumps | 1,9 |
| Turbine journal bearings | 1,10 |
Likewise the speed (N- RPM) can be categorized into Very Low (6), Low (7), Normal (8), High (9), Very High (10) the classification of which is given below:
- N<= 25
- 5 <= N<=100
- 100 <=N <= 1.3 500
- 500 <=N <= 1500
- N:>= 1500
Temperature ranges in various bearings and gears can be classified into Normal (T<60), High (60=T=120), Very High (T>120), Low (T<10), Very Low (T<0). Rolling Mills and Finishing lines in steel plants work under severe moisture condition, therefore rating the moisture level in steel plant equipment become much essential at steel plants. The moisture level (M in ppm) in equipment can be categorized into Normal (M= 100), High (100 =N=500), Very High (M> 500).As various operational groups of a steel plants have distinct operating conditions, a proper lubricant is to be selected taking consideration of not only design parameters but also the operating condition such as the moisture level, dust ingress and acidity/alkalinity of the environment.
Lubrication challenges in a steel plants
 From a lubrication perspective equipment under severe working condition poses serious threat to lubrication failure. Critical parameters of such equipment are
From a lubrication perspective equipment under severe working condition poses serious threat to lubrication failure. Critical parameters of such equipment are
- High speed
- High impact loads
- High temperature
- Ingress of cooling water and scale in the lubricant
- Pumpability problem (Pumping of grease to long distances in CGS systems)
- Ever increasing speeds and loads to improve production rates
For high temperature application a thermally stable highly refined mineral oil with high VI shall be used for temperature range below 100 deg C. For temperature more than 100 deg C synthetic oils shall be used. Mineral oil & synthetic oil for such application may or may not be doped with MoS2 OR PTFE filler. Clay base grease with MoS2 filler can operate up to 150O C where as Li base/poly urea/Li, Al-complex grease can be used when operating temperature is below 130O C. For high temperature application i.e. temperature up to 200O C Ca-Sulfonate greases are suitable. For high impact forces application, high viscosity oil with / without MoS2, graphite, PTFE fillers, EP additive is used. Similarly greases with high viscosity oil (ISO - VG - 320/460/680/1000) are used for high load operation.
Equipment with very high speed requires improved application method as working temperatures tend to rise. Oil mist lubrication helps high speed application. Lubricating oil with low viscosity and inherent heat stability
For water and scale ingress application, installation of water deflectors and application of better polymer sealants shall be done. In oil lubrication system oil with super demulsibility property shall be chosen for such application. In grease lubricating system, the area where maximum water ingress is present especially in mills; Li-Ca mixed base grease can be used to eliminate bearing failure. Li-Ca mixed base greases possess excellent water washout and water spray-off properties which resists washing out of greases from the surface due to ingress of moisture. Greases with high viscosity base oil poses serious problem of pumpability especially at low temperatures. Such applications need to be isolated into separate small systems to cater to short distance pumping. Also multiline grease system can be adopted to obviate such pumpability problem in the grease system.
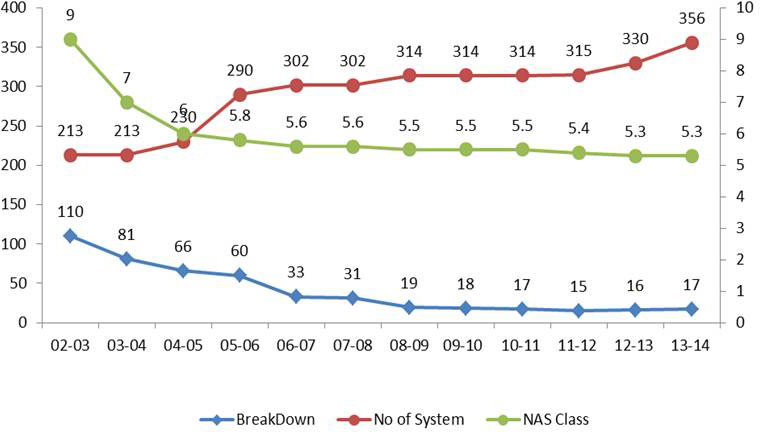 The life of the lubricant and the life of equipment in steel plants are directly proportional to how clean the oil is initially and how effective the procedures are to maintain its cleanliness level. Simply by using cleaner oil equipment life can be enhanced. When the cleanliness of hydraulic fluid in a hydraulic system where servo valves are used for zero tolerance and consistent dimensional parameters is increased by a factor of 10; it has been observed through maintenance practices that pump life can be extended by a factor of 50. Up to 90% reduction in bearing failures can be achieved by a contamination control program. Hydraulic fluid system shall be maintained with cleanliness level of NAS 4 or 5 that to particle of 2-5 Q & 5-15 Q should be below 1500 and 1000 respectively. Filters of beta ratio 1000 are available with dirt holding capacity of 99.9. % can be used now –a- days to contain contamination. Apart from contamination control, condition monitoring program for lubricant can enhance the reliability factor in equipment. It also optimizes the usage of a lubricant in the equipment without compromising the quality. Condition monitoring program for lubricants includes performance parameters analysis of lubricants and wear debris analysis.
The life of the lubricant and the life of equipment in steel plants are directly proportional to how clean the oil is initially and how effective the procedures are to maintain its cleanliness level. Simply by using cleaner oil equipment life can be enhanced. When the cleanliness of hydraulic fluid in a hydraulic system where servo valves are used for zero tolerance and consistent dimensional parameters is increased by a factor of 10; it has been observed through maintenance practices that pump life can be extended by a factor of 50. Up to 90% reduction in bearing failures can be achieved by a contamination control program. Hydraulic fluid system shall be maintained with cleanliness level of NAS 4 or 5 that to particle of 2-5 Q & 5-15 Q should be below 1500 and 1000 respectively. Filters of beta ratio 1000 are available with dirt holding capacity of 99.9. % can be used now –a- days to contain contamination. Apart from contamination control, condition monitoring program for lubricant can enhance the reliability factor in equipment. It also optimizes the usage of a lubricant in the equipment without compromising the quality. Condition monitoring program for lubricants includes performance parameters analysis of lubricants and wear debris analysis.
Lubrication in an integrated steel plant is a major challenge with numerous types of lubricants and various types of equipment. The steel plant equipment work under various operating parameters; like from extreme heavy load to very high speed, low temperatures to high temperatures, dusty polluted environment to humid acid environment. Therefore proper selection of lubricant is much essential for smooth operation in steel plants and reliability of equipment. A good lubricant can be of slightly higher cost. However, its benefits in terms of equipment reliability, productivity, reduction in down time are substantial.
